Bayesian Game
- Extensive Form Game을 통해 Imperfect information이 존재하는, 즉 하나의 information set에 여러 개의 노드가 존재하는(=player가 상대방의 이전 action을 모르는) game을 다뤘다.
- 이번에는 Incmplete information이 존재한다. 각 player들에게 Type이라는 새로운 속성이 생긴다.
- 각 유저들의 type을 나타내는 새로운 component T={Ti}i∈N 를 도입하게 되고
- payoff는 u:S×T→Rn 와 같이 표현할 수 있다.
Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE)
- 각 player들은 자신의 type에 따라 strategy를 잘 선택해서(σi∗:Ti→Δ(Si)) Expected utility를 극대화한다.
- 이 때 Expected Utility E[ui(σi,σ−i∗(t−i),t)∣ti]=∑t−i∈T−ip(t−i∣ti)ui(σi,σ−i∗(t−i),t)
- 아래 Cournot Competition 예시가 이 수식을 이해하기 좋았다.
Example (Cournot Competition)
기업1, 기업2의 Marginal Cost는 각각의 type Ti∈{H,L}에 따라 ci∈{ciH,ciL} 이다. 두 기업은 각자의 생산량 qiH∈[0,∞),qiL∈[0,∞) 을 결정하고, payoff는 qi(1−Q−ci) 이다. (Q=q1+q2) 두 기업은 동시에 생산량을 선택한다(=static). 다음의 확률은 주어져있다고 하자.
- p(c1H,c2H),p(c1L,c2L)=21α
- p(c1H,c2L),p(c1L,c2H)=21(1−α)
그럼 두 기업이 각각 H,L의 타입일 경우에 따라 4가지의 payoff를 계산할 수 있다.
-
기업1이 H type인 경우, 기업1의 payoff
E1[u1(σ1,σ2∗(t2),t)∣t1=H]=∑t2∈T2p(t2∣t1=H)u1(σ1,σ2∗(t2),t) 이다.
t2∈{H,L} 이므로 위 시그마는 두 가지 경우에 대해 풀어내면 된다.
E1[u1(σ1,σ2∗(t2),t)∣t1=H]=p(t2=H∣t1=H)u1(σ1,σ2∗(t2=H),t)+p(t2=L∣t1=H)u1(σ1,σ2∗(t2=L),t)
위 식의 p(t2=H∣t1=H),p(t2=L∣t1=H) 는 Bayes' rule로 구하면
-
p(t2=H∣t1=H)=p(t1=H)p(t2=H,t1=H)=p(t1=H,t2=H)+p(t1=H,t2=L)p(t2=H,t1=H)=21α+21(1−α)21α=α
-
p(t2=L∣t1=H)=p(t1=H)p(t2=L,t1=H)=p(t1=H,t2=H)+p(t1=H,t2=L)p(t2=L,t1=H)=21α+21(1−α)21(1−α)=(1−α)
이제 대입해서 payoff를 극대화하는 optimization 식을 써내면
qiHmax=α(1−(q2H+q1H)−c1H)q1H+(1−α)(1−(q2L+q1H)−c1H)q1H
이고, 여기에 FOC를 적용하면
q1H=21(1−αq2H−(1−α)q2H−c1H)
이 나온다.
-
기업1이 L type인 경우, 기업1의 payoff
E1[u1(σ1,σ2∗(t2),t)∣t1=L]=∑t2∈T2p(t2∣t1=L)u1(σ1,σ2∗(t2),t) 이고, 다음 과정들은 모두 동일하다.
-
기업2가 L type인 경우, 기업2의 payoff
-
기업2가 L type인 경우, 기업2의 payoff
이렇게 4개의 식을 도출해내면, 미지수의 개수가 q1H,q1L,q2H,q2L 4개이므로 해를 구할 수 있다.
Example (Cutoff strategy)
일단 생략
Example (Auction)
일단 생략
Harsanyi Transformation
player의 type이 확률적으로 결정되는 경우에, 이에 대해 Nature를 도입하여 모델링할 수 있다. player가 하나 늘어난 것과 같은 모양새가 된다.
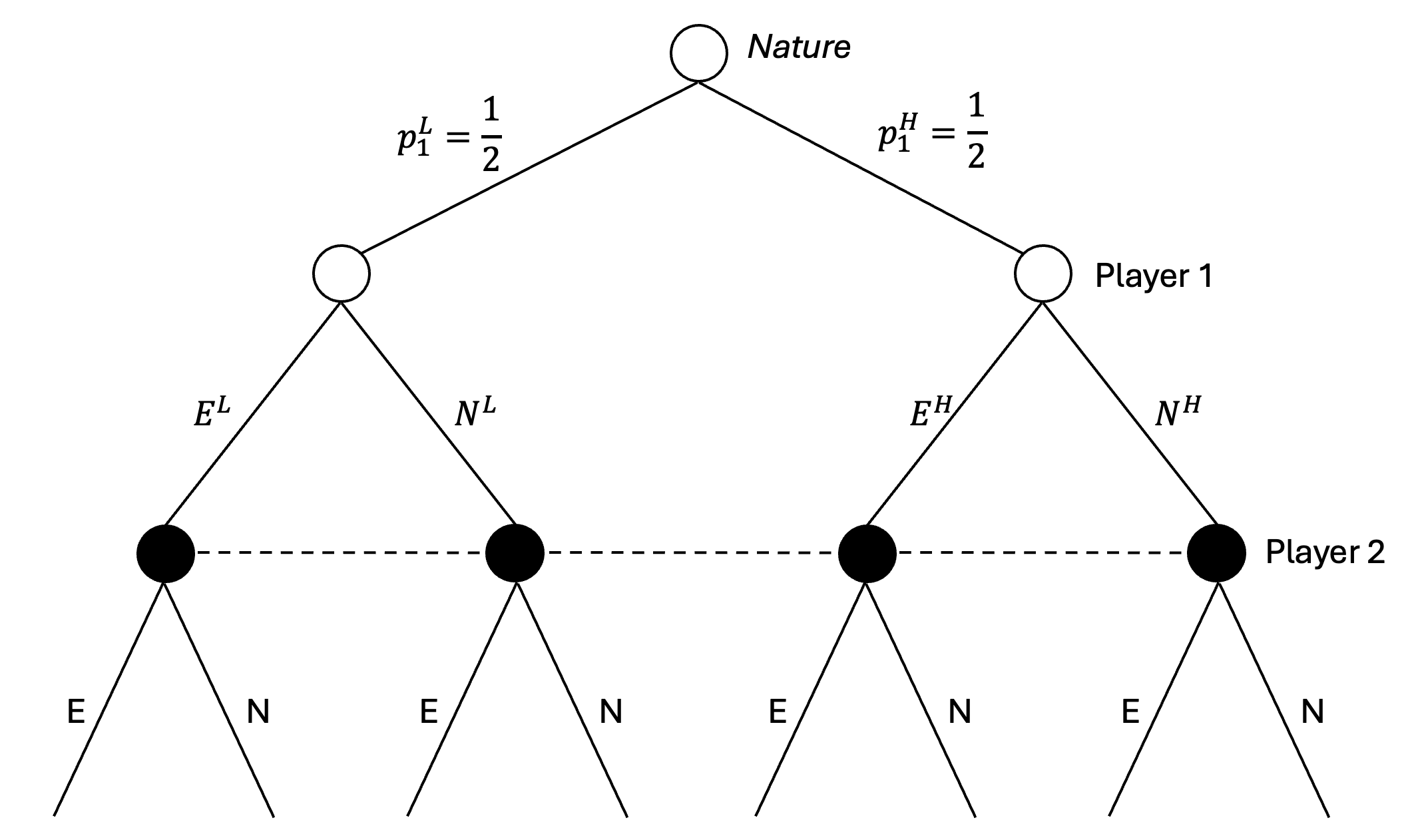
Example (Entry game)
2024.06.23

